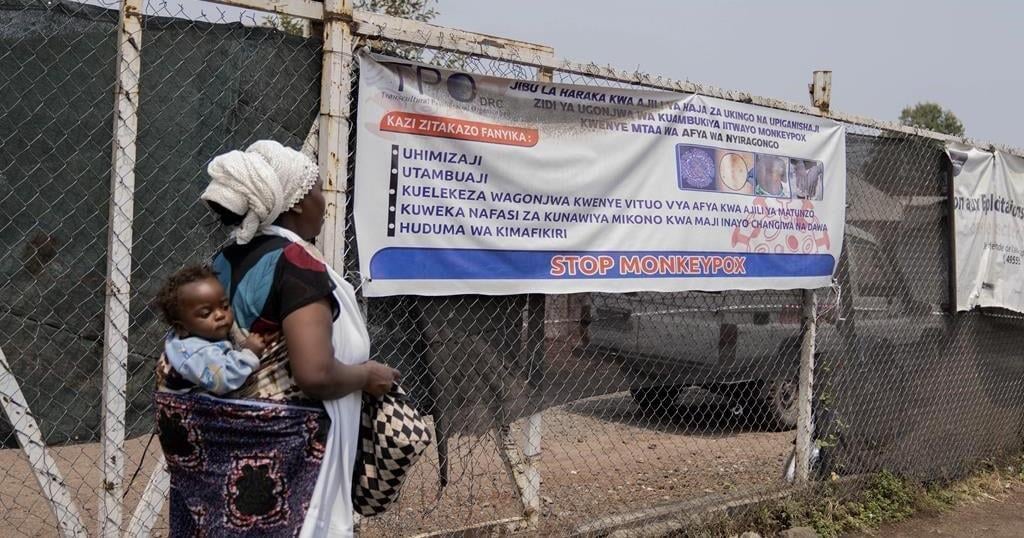
The Canadian government says it will donate up to 200,000 vaccine doses to fight the mpox outbreak in Congo and other African countries.
It says the donated doses of Imvamune will come from Canada’s existing supply and will not affect the country’s preparedness for mpox cases in this country.
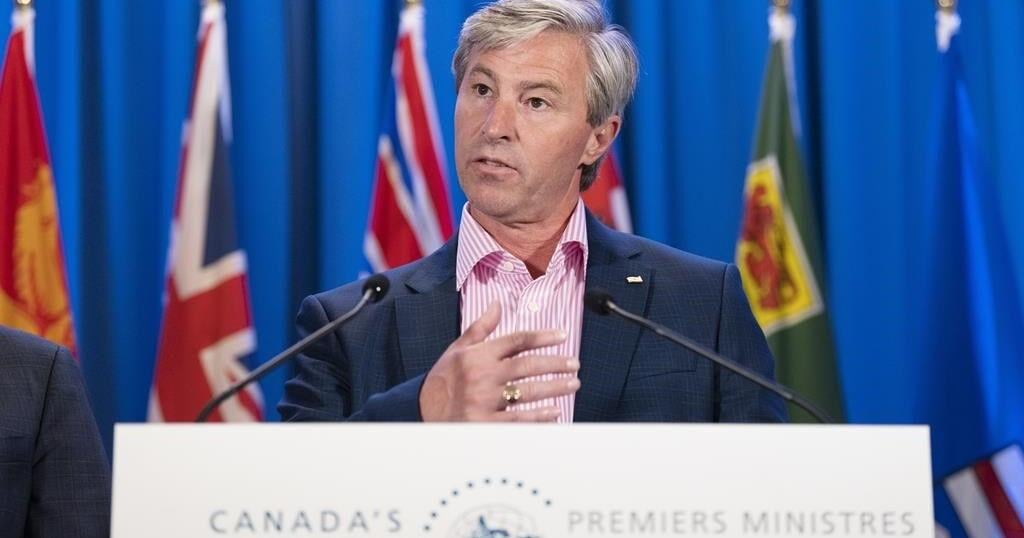
Minister of Health Mark Holland says the donation “will help to protect those in the most affected regions of Africa and will help prevent further spread of the virus.”
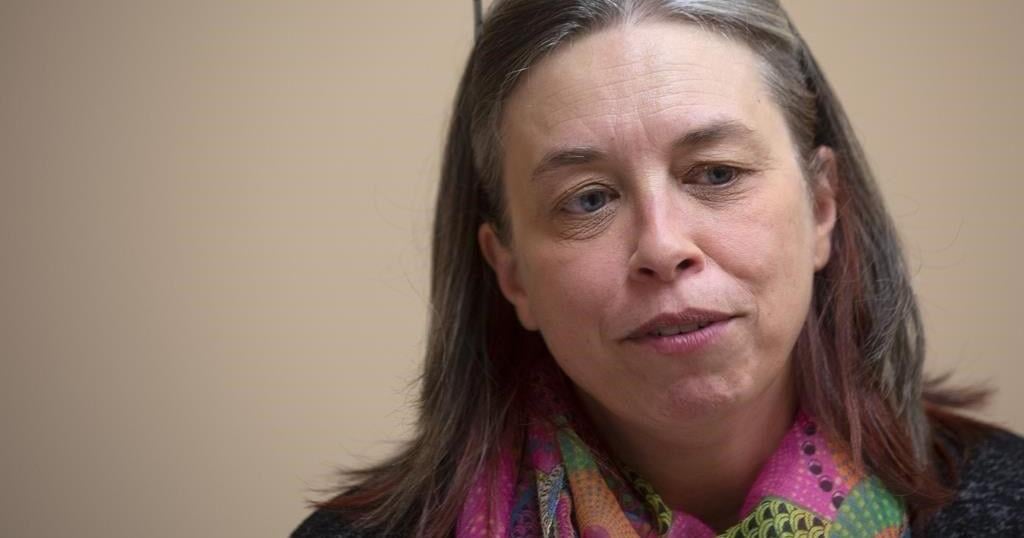
Dr. Madhukar Pai, Canada research chair in epidemiology and global health, says although the donation is welcome, it is a very small portion of the estimated 10 million vaccine doses needed to control the outbreak.
Vaccine donations from wealthier countries have only recently started arriving in Africa, almost a month after the World Health Organization declared the mpox outbreak a public health emergency of international concern.
A few days after the declaration in August, Global Affairs Canada announced a contribution of $1 million for mpox surveillance, diagnostic tools, research and community awareness in Africa.
On Thursday, the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention said mpox is still on the rise and that testing rates are “insufficient” across the continent.
Jason Kindrachuk, Canada research chair in emerging viruses at the University of Manitoba, said donating vaccines, in addition to supporting surveillance and diagnostic tests, is “massively important.”
But Kindrachuk, who has worked on the ground in Congo during the epidemic, also said that the international response to the mpox outbreak is “better late than never (but) better never late.”
“It would have been fantastic for us globally to not be in this position by having provided doses a much, much longer time prior than when we are,” he said, noting that the outbreak of clade I mpox in Congo started in early 2023.
Clade II mpox, endemic in regions of West Africa, came to the world’s attention even earlier — in 2022 — as that strain of virus spread to other countries, including Canada.
Two doses are recommended for mpox vaccination, so the donation may only benefit 100,000 people, Pai said.
Pai questioned whether Canada is contributing enough, as the federal government hasn’t said what percentage of its mpox vaccine stockpile it is donating.
“Small donations are simply not going to help end this crisis. We need to show greater solidarity and support,” he said in an email.
“That is the biggest lesson from the COVID-19 pandemic — our collective safety is tied with that of other nations.”
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Sept. 13, 2024.
Canadian Press health coverage receives support through a partnership with the Canadian Medical Association. CP is solely responsible for this content.