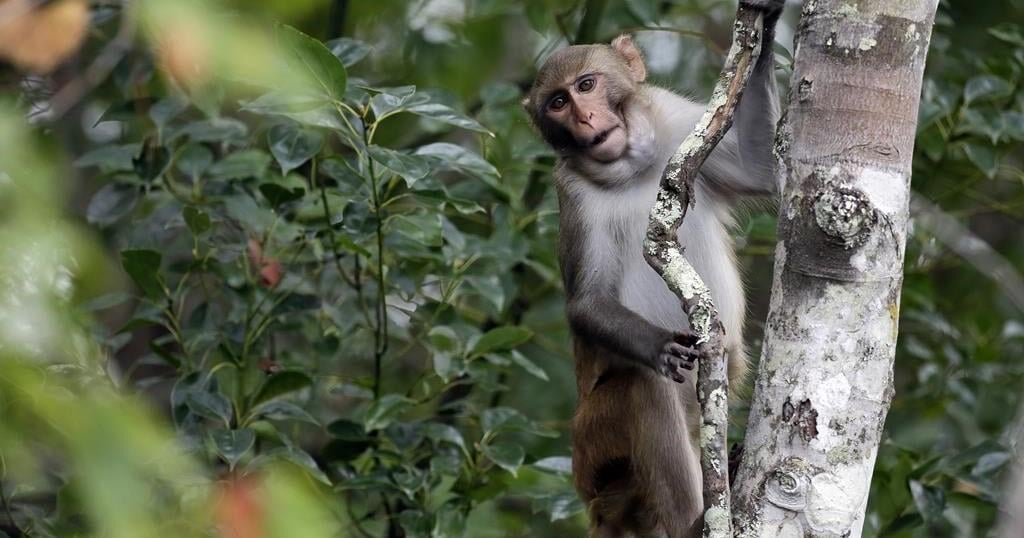
COLUMBIA, S.C. (AP) — Forty-three monkeys bred for medical research that escaped a compound in South Carolina have been spotted in the woods near the site and workers are using food to try to recapture them, authorities said Friday.
The Rhesus macaques made a break for it Wednesday after an employee at the Alpha Genesis facility in Yemassee didn’t fully lock a door as she fed and checked on them, officials said.
“They are very social monkeys and they travel in groups, so when the first couple go out the door the others tend to just follow right along,” Alpha Genesis CEO Greg Westergaard told CBS News.
Westergaard said his main goal is to have the monkeys returned safely with no other problems. “I think they are having an adventure,” he said.
The monkeys on Friday were exploring the outer fence of the Alpha Genesis compound and are cooing at the monkeys inside, police said in a statement.
“The primates are exhibiting calm and playful behavior, which is a positive indication,” the police statement said, adding company workers are closely watching the monkeys while keeping their distance as they work to safely recapture them.
The monkeys are about the size of a cat. They are all females weighing about 7 pounds (3 kilograms).
Alpha Genesis, federal health officials and police all said the monkeys pose no risk to public health. The facility breeds the monkeys to sell to medical and other researchers.
“They are not infected with any disease whatsoever. They are harmless and a little skittish,” Yemassee Police Chief Gregory Alexander said Thursday.
Authorities still recommend that people who live near the compound about 1 mile (1.6 kilometers) from downtown Yemassee shut their windows and doors and call 911 if they see the monkeys. Approaching them could make them more skittish and harder to capture, officials said.
Eve Cooper, a biology professor at the University of Colorado Boulder who has studied rhesus macaques, said the animals have the potential to be dangerous and urged people to keep their distance.
Rhesus macaques monkeys can be aggressive. And some carry the herpes B virus, which can be fatal to humans, Cooper said.
However, Alpha Genesis states on its website that it specializes in pathogen-free primates. Cooper noted that there are pathogen-free populations of rhesus macaques that have been quarantined and tested.
“I would give them a wide berth,” Cooper said. “They’re unpredictable animals. And they can behave quite aggressively when they’re afraid.”
Alpha Genesis provides primates for research worldwide at its compound about 50 miles (80 kilometers) northeast of Savannah, Georgia, according to its website.
Locally, it is known as “the monkey farm.” And there is more amusement than panic around Yemassee and its population of about 1,100 just off Interstate 95 about 2 miles from Auldbrass Plantation, a Frank Lloyd Wright house designed in the 1930s.
There have been escapes before, but the monkeys haven’t caused problems, said William McCoy, who owns Lowcountry Horology, a clock and watch repair shop.
“They normally come home because that’s where the food is,” he said.
McCoy has lived in Yemassee for about two years and while he plans to stay away from the monkeys, he has his own light-hearted plan to get them back.
“I’m stocking up bananas, maybe they’ll show up,” McCoy said.
The Alpha Genesis compound is regularly inspected by federal officials.
In 2018, the U.S. Department of Agriculture fined Alpha Genesis $12,600 in part after officials said 26 primates escaped from the Yemassee facility in 2014 and an additional 19 got out in 2016.
The company’s fine was also issued because of individual monkey escapes as well as the killing of one monkey by others when it was placed in the wrong social group, according to a report from the USDA.
The group Stop Animal Exploitation Now sent a letter Thursday to the USDA asking the agency to immediately send an inspector to the Alpha Genesis facility, conduct a thorough investigation and treat them as a repeated violator. The group was involved in the 2018 fine against the company.
“The clear carelessness which allowed these 40 monkeys to escape endangered not only the safety of the animals, but also put the residents of South Carolina at risk,” wrote Michael Budkie, executive director of the group.
The USDA, which has inspected the compound 10 times since 2020, didn’t immediately respond to the letter.
The facility’s most recent federal inspection in May showed there were about 6,700 primates on site and no issues.
In a 2022 review, federal veterinarians reported two animals died when their fingers were trapped in structures and they were exposed to harsh weather. They also found cages weren’t adequately secure. Inspectors said criminal charges, civil penalties or other sanctions could follow if the problems weren’t fixed.
Since then, Alpha Genesis has undergone six inspections with minor problems reported only once.
In January 2023, the USDA said temperatures were out of the 45 to 85 degree Fahrenheit (7.2 to 29.5 degree Celsius) required range at some of the compound’s monkey cages. The inspection found moldy food in one bin, sharp edges on a gate that could cut an animal and sludge, food waste, used medical supplies, mechanical equipment, and general construction debris on the grounds.
Supporters of medical research involving nonhuman primates said they are critical to lifesaving medical advances like creating vaccines against COVID-19 because of their similarities to people. Keeping a domestic supply of the animals is critical to prevent shortages for U.S. researchers.
Humans have been using the rhesus macaque for scientific research since the late 1800s. Scientists believe that rhesus macaques and humans split from a common ancestor about 25 million years ago and share about 93% of the same DNA.
These monkeys have been launched into space on V2 rockets, used for AIDS research, had their genome mapped and made stars of their own reality television show. They were in such high demand in the early 2000s that a shortage led to scientists paying up to $10,000 per animal.
Outside of rats and mice, rhesus macaques are one of the most studied animals on the planet, said Dario Maestripieri, a behavioral scientist at the University of Chicago who wrote the 2007 book “Macachiavellian Intelligence: How Rhesus Macaques and Humans Have Conquered the World.”
The animals are very family oriented, siding with relatives when fights break out. And they’re adept at building political alliances in the face of threats from other monkeys. But they can be painful to watch. Monkeys with lower status in the hierarchy live in a constant state of fear and intimidation, Maestripieri said.
“In some ways, they kind of represent some of the worst aspects of human nature,” Maestripieri said.
___
Lovan reported from Louisville, Kentucky, and Finley reported from Norfolk, Virginia.

 Predictions from HelpSeeker’s AI on how many people in Canada that will be homeless by 2030. (HelpSeeker)
Predictions from HelpSeeker’s AI on how many people in Canada that will be homeless by 2030. (HelpSeeker) HelpSeeker’s predictive AI and researchers believe Canada needs to invest about $169 million to close the gap for homelessness. (HelpSeeker)
HelpSeeker’s predictive AI and researchers believe Canada needs to invest about $169 million to close the gap for homelessness. (HelpSeeker)