Health
US urges Tanzania to embrace COVID-19 vaccines, share data – Burnaby Now

NAIROBI, Kenya — The United States praised Tanzania on Friday for finally acknowledging the resurgence of COVID-19 after claiming for months it had defeated the pandemic through prayer. But the U.S. urged the country to share infection data and accept vaccines.
“It has become clear that the virus variant has arrived in Tanzania,“ U.S. Ambassador Donald Wright, who is also a doctor, said in a statement. “I’ve been encouraged by recent statements from the Ministry of Health acknowledging COVID-19 as a public health priority in Tanzania and urging citizens to take basic precautions.“
Tanzania is one of Africa’s most populous countries, with some 60 million people, and during its long COVID-19 denial the director of the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention warned that if the continent isn’t united, “it’s doomed.”
High-profile deaths this month in the East African nation, including that of the vice-president of the semi-autonomous island region of Zanzibar, appeared to lead populist President John Magufuli to acknowledge publicly in the past week that COVID-19 was back.
For weeks, Tanzanians had seen a rise in death notices citing breathing difficulties and cases of what health workers called “pneumonia.” But countries such as Oman reported Tanzanians arriving in their countries and testing positive for the virus.
Meanwhile, Tanzania’s president openly questioned COVID-19 vaccines, without providing evidence. Tanzania is one of the very few countries in Africa that has not signed up for the global COVAX facility to provide vaccines to low- and middle-income countries. Now those vaccines have begun to arrive, in Ghana and Ivory Coast, with more on the way.
The U.S. ambassador’s statement urges Tanzania to “convene its health experts and review the evidence on vaccines.” He also notes “it is critical to collect and report information about testing and cases.“
Tanzania last updated its number of infections last April. That number remains at 509.
Then the ambassador turned to aid: “Here in Tanzania, we dedicated $16.4 million to mitigate the COVID-19 pandemic since the first confirmed case was diagnosed in March of 2020. The United States stands ready to ramp up our efforts and we are committed to working side by side with Tanzania to defeat COVID-19.”
An embassy spokesman did not immediately respond to a question about whether further aid depends on Tanzania sharing pandemic data and embracing vaccines.
Tanzania, unlike other African countries, did not lock down during the pandemic and it has promoted that to tourists and others.
In an interview with The Associated Press on Thursday, Tanzania’s investment minister, Kitila Mkumbo, asserted that COVID-19 “has not been one of the major concerns of investors.” He added that American investors “are waiting for the pandemic to slow down so movement can begin.”
And the minister welcomed the Biden administration, saying he believed that the U.S. will once again “take global responsibility of supporting developing countries like Tanzania in many aspects, like health.”
___
Follow all of AP’s pandemic coverage at https://apnews.com/hub/coronavirus-pandemic, https://apnews.com/hub/coronavirus-vaccine and https://apnews.com/UnderstandingtheOutbreak
Cara Anna, The Associated Press
Health
Quebec successfully pushes back against rise in measles cases – CBC.ca
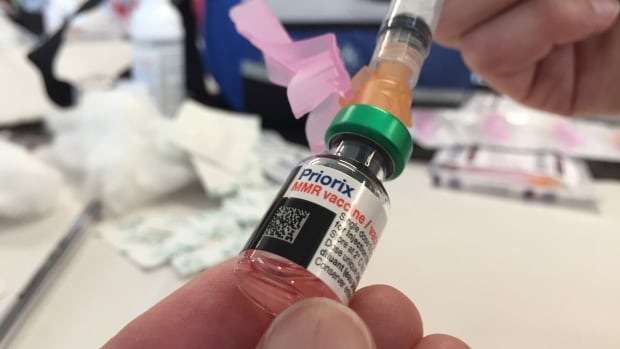

Quebec appears to be winning its battle against the rising tide of measles after 45 cases were confirmed province-wide this year.
“We’ve had no locally transmitted measles cases since March 25, so that’s good news,” said Dr. Paul Le Guerrier, responsible for immunization for Montreal Public Health.
There are 17 patients with measles in Quebec currently, and the most recent case is somebody who was infected while abroad, he said.
But it was no small task to get to this point.
Le Guerrier said once local transmission was detected, news was spread fast among health centres to ensure proper protocols were followed — such as not letting potentially infected people sit in waiting rooms for hours on end.
Then about 90 staffers were put to work, tracking down those who were in contact with positive cases and are not properly vaccinated. They were given post-exposure prophylaxis, which prevents disease, said Le Guerrier.
From there, a vaccination campaign was launched, especially in daycares, schools and neighbourhoods with low inoculation rates. There was an effort to convince parents to get their children vaccinated.
Vaccination in schools boosted
Some schools, mostly in Montreal, had vaccination rates as low as 30 or 40 per cent.
“Vaccination was well accepted and parents responded well,” said Le Guerrier. “Some schools went from very low to as high as 85 to 90 per cent vaccination coverage.”
But it’s not only children who aren’t properly vaccinated. Le Guerrier said people need two doses after age one to be fully inoculated, and he encouraged people to check their status.
There are all kinds of reasons why people aren’t vaccinated, but it’s only about five per cent who are against immunization, he said. So far, some 10,000 people have been vaccinated against measles province-wide during this campaign, Le Guerrier said.
The next step is to continue pushing for further vaccination, but he said, small outbreaks are likely in the future as measles is spreading abroad and travellers are likely to bring it back with them.
Need to improve vaccination rate, expert says
Dr. Donald Vinh, an infectious diseases specialist from the McGill University Health Centre, said it’s not time to rest on our laurels, but this is a good indication that public health is able to take action quickly and that people are willing to listen to health recommendations.
“We are not seeing new cases or at least the new cases are not exceeding the number of cases that we can handle,” said Vinh.
“So these are all reassuring signs, but I don’t think it’s a sign that we need to become complacent.”
Vinh said there are also signs that the public is lagging in vaccine coverage and it’s important to respond to this with improved education and access. Otherwise, microbes capitalize on our weaknesses, he said.
Getting vaccination coverage up to an adequate level is necessary, Vinh said, or more small outbreaks like this will continue to happen.
“And it’s very possible that we may not be able to get one under control if we don’t react quickly enough,” he said.
Health
Pregnant women in the Black Country urged to get whooping cough vaccine – BBC.com


Pregnant women urged to get whooping cough vaccine
Pregnant women in the Black Country are being urged to get vaccinated against whooping cough after a rise in cases.
The bacterial infection of the lungs spreads very easily and can cause serious problems, especially in babies and young children.
The Black Country Integrated Care Board (ICB) is advising pregnant women between 16 and 32 weeks to contact their GP to get the vaccine so their baby has protection from birth.
The UK Health Security Agency warned earlier this year of a steady decline in uptake of the vaccine in pregnant women and children.
Symptoms of the infection, also known as “100-day cough”, are similar to a cold, with a runny nose and sore throat.
Sally Roberts, chief nursing officer for the ICB, which covers Wolverhampton, Dudley, Walsall and Sandwell, said anyone could catch it, but it was more serious for young children and babies.
“Getting vaccinated while you’re pregnant is highly effective in protecting your baby from developing whooping cough in the first few weeks of their life – ideally from 16 weeks up to 32 weeks of pregnancy,” she said.
“If for any reason you miss having the vaccine, you can still have it up until you go into labour.”
Follow BBC West Midlands on Facebook, X and Instagram. Send your story ideas to: newsonline.westmidlands@bbc.co.uk
Health
Measles cases stabilize in Montreal – CityNews Montreal


The number of measles cases has stabilized, according to the Montreal Public Health.
Since March 25, there have been no contaminations reported within the community.
“Our teams have identified all contact cases of measles,” said media relations advisor Geneviève Paradis. “It’s a laborious task: each measles case produces hundreds of contacts.”
All community transmission cases since February 2024 have been caused by returning travelers who were either unvaccinated or partially vaccinated.
Currently, there are 18 measles cases in Montreal – with 46 total in Quebec. This according to the April 18 figures from the provincial government.
“With the summer vacations approaching, if you’re travelling, it is essential to check if you are protected against measles,” explained Paradis.
According to Montreal Public Health, a person needs to have received two doses after the age of 12 months to be immunized against the virus.
They’ve launched a vaccination campaign throughout the region, and currently, 11,341 people have been vaccinated against measles in Montreal between March 19 and April 15.
Vaccination is also being provided in schools and at local service points.
“The vaccination operation is under the responsibility of the five CIUSSS of the territory,” concluded Paradis.
-



 Science7 hours ago
Science7 hours agoJeremy Hansen – The Canadian Encyclopedia
-



 Investment7 hours ago
Investment7 hours agoUK Mulls New Curbs on Outbound Investment Over Security Risks – BNN Bloomberg
-



 Health20 hours ago
Health20 hours agoSupervised consumption sites urgently needed, says study – Sudbury.com
-



 Tech6 hours ago
Tech6 hours agoSave $700 Off This 4K Projector at Amazon While You Still Can – CNET
-



 Sports5 hours ago
Sports5 hours agoAuston Matthews denied 70th goal as depleted Leafs lose last regular-season game – Toronto Sun
-
News20 hours ago
Canada's 2024 budget announces 'halal mortgages'. Here's what to know – National Post
-



 Tech5 hours ago
Tech5 hours ago'Kingdom Come: Deliverance II' Revealed In Epic New Trailer And It Looks Incredible – Forbes
-



 Science20 hours ago
Science20 hours agoGiant, 82-foot lizard fish discovered on UK beach could be largest marine reptile ever found – Livescience.com





