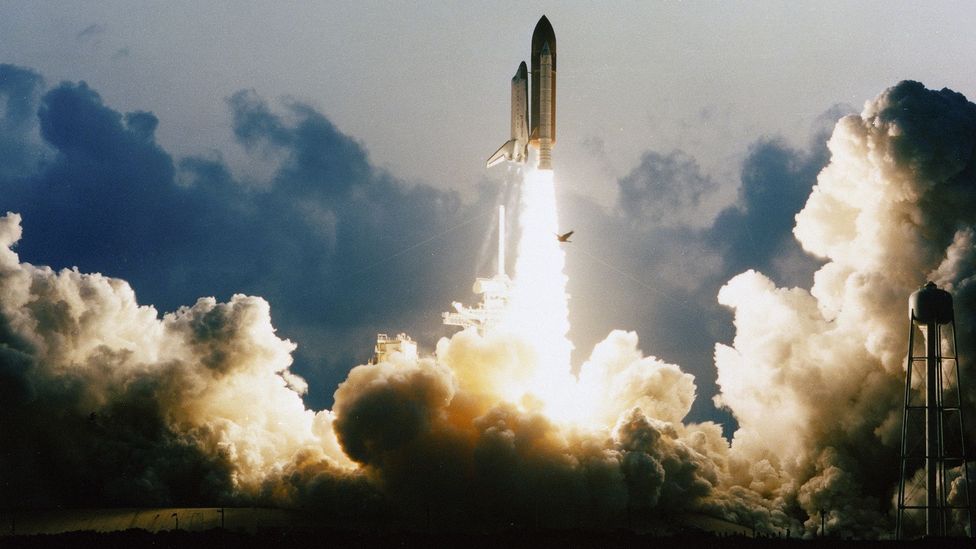
Watch footage of the Saturn V launches during Nasa’s Apollo programme in the 1960s and 1970s, and one thing that may strike you – even more than the polyester-heavy fashions and retro haircuts – is just how far away the crowds of onlookers are from the main event.
There were several good reasons for this, and noise was one of them: loud sounds can kill, and few things built by humans have been as loud as the Saturn V.
When Apollo astronauts blasted off on their missions to the Moon, they did so with more than 3.2 miles (5.1km) separating them from the excited, onlooking crowds. Even at such distances, the noise was incredible. A common myth at the time was that the soundwaves from the Saturn V’s engines were so powerful that they melted concrete on the launch pad and set fire to grass a mile (1.6km) away (both were false).
Nasa’s measurements at the time captured the launch noise at 204 decibels. Compare that to the sound of a jet airliner taking off, which is between 120 and 160 decibels and considered dangerous to hearing if endured for longer than 30 seconds. Even 1.5 miles (2.4km) away, the noise from a Saturn V launch was recorded as being 120 decibels – as loud as a rock concert, or a car horn at very close quarters.
“I’m always struck by the physicality of a launch,” says Anthony Rue, a Florida café owner who has been watching and photographing launches since the days of Saturn V. “Back in the 1970s there was an audio device called Sensurround that was used in disaster movies like Earthquake to create a subsonic seismic ‘experience’ in the theatre.
“Launches, from up close, are a bit like Sensurround,” says Rue. “You can feel a slight tremble, then a building rumble in your chest before you can hear any actual sound. The subsonic bass frequencies make your ears crackle. After a few seconds, the sound coalesces into a roar, like a massive welding torch.”
You might also like:
- Inside Nasa’s giant rocket factory
- Artemis I: A giant rocket to set records
- The genius behind early Russian space tech
Last year, a team of scientists from Brigham Young University in Utah calculated just how loud Saturn V was. They came up with a remarkably similar finding to Nasa’s own recordings – 203 decibels.
The difference between 160 and 200-odd decibels might not sound like a lot in the grand scheme of things, but it is.
“One hundred and seventy decibels would be equivalent to 10 aircraft engines. Two hundred would be 10,000 engines,” said Kent Gee, leader author of the study and professor of physics at the Brigham Young University at the time. “Every 10 decibels is an order-of-magnitude increase.”