Geological research spanning more than a decade found Saskatchewan has one of the rarest kinds of impact craters on Earth.
Science
Gow Lake crater in Saskatchewan a rarity on Earth

At its geological core, the lake — located in remote wilderness about 400 kilometres north of the town of Nipawin — holds unique features that are unparalleled on Earth, according to research led by Dr. Gordon Osinski at Western University in London, Ont. Osinski is an international expert on impact cratering.
What makes the Gow Lake crater unique, Osinski said in an interview, is that despite its age, the crater holds remarkably well-preserved rocks and rock formations that are extraordinary.
Whatever hit the Earth at that spot, whether asteroid or comet, generated so much energy that it liquified the Earth’s crust and created rock of a different kind.
“Gow Lake has a lot of these very interesting rocks we call impactites,” Osinski said. “Because of the nature of the impact process, the melt-rock, or breccia, we find at Gow Lake make it unique in the world. You will not find another rock that looks like it anywhere else on Earth.”
Since the 1970s, it has been known that the water in Gow Lake fills an impact crater measuring roughly five kilometres across. It was assumed to be a central peak impact structure — a common form of crater, circular in shape, with terraced walls and a peak in the middle.
In 2011, a team of researchers lead by Osinski, a planetary geologist at Western, conducted a field study at Gow Lake. The unusual characteristics of the crater prompted long-term study, mostly carried out in the lab.
A dozen years later — the blink of an eye in geological time — the team’s findings were published this week in the journal Meteoritics & Planetary Science. They show that the Gow Lake crater is far from typical and is actually a transitional impact structure, of which there are only two on Earth.
“Being rare on Earth is one of the significant things about this crater,” Osinski said. “I would say it is the only actual example we have of this type of crater. The only other crater of its kind, in Australia, is quite eroded and there’s very little information left.”
A transitional crater is characterized by fairly smooth walls and a floor partially or entirely covered by debris fallen from the crater walls. It is a transitional form between a simple bowl-shaped crater and a complex crater with a central uplift.
“That projectile hits the surface of the Earth, penetrates somewhat and is essentially vaporized,” he said. “It’s all about kinetic energy. That thing is coming in staggeringly fast, 15 to 20 kilometres per second, with a huge amount of energy. That energy is left over as heat that can literally melt cubic kilometres of the Earth’s crust, instantly. The surrounding rock looks like volcanic rock.”
The asteroid or comet itself would have been small compared to the size of the crater — one-10th or one-20th the size.
“We know of about 200 meteorite impact craters on Earth, but many of them are buried, submerged or eroded to such a degree that there’s hardly anything left to study,” said Osinski.
Osinski added that Saskatchewan is a hotspot for impact craters in the country.
Canada is also home to one of the only human-inhabited impact craters in the world. The city of Greater Sudbury, a hotbed of nickel mining, is situated in the Sudbury Basin, a crater 130 kilometres in diameter dating back 1.8 billion years.

News
Here’s how Helene and other storms dumped a whopping 40 trillion gallons of rain on the South
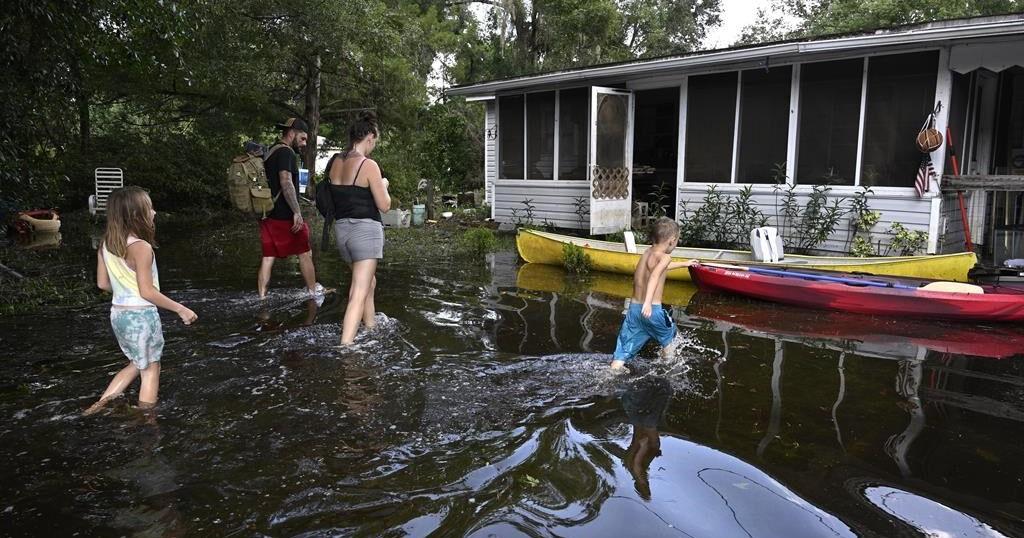

More than 40 trillion gallons of rain drenched the Southeast United States in the last week from Hurricane Helene and a run-of-the-mill rainstorm that sloshed in ahead of it — an unheard of amount of water that has stunned experts.
That’s enough to fill the Dallas Cowboys’ stadium 51,000 times, or Lake Tahoe just once. If it was concentrated just on the state of North Carolina that much water would be 3.5 feet deep (more than 1 meter). It’s enough to fill more than 60 million Olympic-size swimming pools.
“That’s an astronomical amount of precipitation,” said Ed Clark, head of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s National Water Center in Tuscaloosa, Alabama. “I have not seen something in my 25 years of working at the weather service that is this geographically large of an extent and the sheer volume of water that fell from the sky.”
The flood damage from the rain is apocalyptic, meteorologists said. More than 100 people are dead, according to officials.
Private meteorologist Ryan Maue, a former NOAA chief scientist, calculated the amount of rain, using precipitation measurements made in 2.5-mile-by-2.5 mile grids as measured by satellites and ground observations. He came up with 40 trillion gallons through Sunday for the eastern United States, with 20 trillion gallons of that hitting just Georgia, Tennessee, the Carolinas and Florida from Hurricane Helene.
Clark did the calculations independently and said the 40 trillion gallon figure (151 trillion liters) is about right and, if anything, conservative. Maue said maybe 1 to 2 trillion more gallons of rain had fallen, much if it in Virginia, since his calculations.
Clark, who spends much of his work on issues of shrinking western water supplies, said to put the amount of rain in perspective, it’s more than twice the combined amount of water stored by two key Colorado River basin reservoirs: Lake Powell and Lake Mead.
Several meteorologists said this was a combination of two, maybe three storm systems. Before Helene struck, rain had fallen heavily for days because a low pressure system had “cut off” from the jet stream — which moves weather systems along west to east — and stalled over the Southeast. That funneled plenty of warm water from the Gulf of Mexico. And a storm that fell just short of named status parked along North Carolina’s Atlantic coast, dumping as much as 20 inches of rain, said North Carolina state climatologist Kathie Dello.
Then add Helene, one of the largest storms in the last couple decades and one that held plenty of rain because it was young and moved fast before it hit the Appalachians, said University of Albany hurricane expert Kristen Corbosiero.
“It was not just a perfect storm, but it was a combination of multiple storms that that led to the enormous amount of rain,” Maue said. “That collected at high elevation, we’re talking 3,000 to 6000 feet. And when you drop trillions of gallons on a mountain, that has to go down.”
The fact that these storms hit the mountains made everything worse, and not just because of runoff. The interaction between the mountains and the storm systems wrings more moisture out of the air, Clark, Maue and Corbosiero said.
North Carolina weather officials said their top measurement total was 31.33 inches in the tiny town of Busick. Mount Mitchell also got more than 2 feet of rainfall.
Before 2017’s Hurricane Harvey, “I said to our colleagues, you know, I never thought in my career that we would measure rainfall in feet,” Clark said. “And after Harvey, Florence, the more isolated events in eastern Kentucky, portions of South Dakota. We’re seeing events year in and year out where we are measuring rainfall in feet.”
Storms are getting wetter as the climate change s, said Corbosiero and Dello. A basic law of physics says the air holds nearly 4% more moisture for every degree Fahrenheit warmer (7% for every degree Celsius) and the world has warmed more than 2 degrees (1.2 degrees Celsius) since pre-industrial times.
Corbosiero said meteorologists are vigorously debating how much of Helene is due to worsening climate change and how much is random.
For Dello, the “fingerprints of climate change” were clear.
“We’ve seen tropical storm impacts in western North Carolina. But these storms are wetter and these storms are warmer. And there would have been a time when a tropical storm would have been heading toward North Carolina and would have caused some rain and some damage, but not apocalyptic destruction. ”
___
Follow AP’s climate coverage at https://apnews.com/hub/climate
___
Follow Seth Borenstein on Twitter at @borenbears
___
Associated Press climate and environmental coverage receives support from several private foundations. See more about AP’s climate initiative here. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Science
‘Big Sam’: Paleontologists unearth giant skull of Pachyrhinosaurus in Alberta
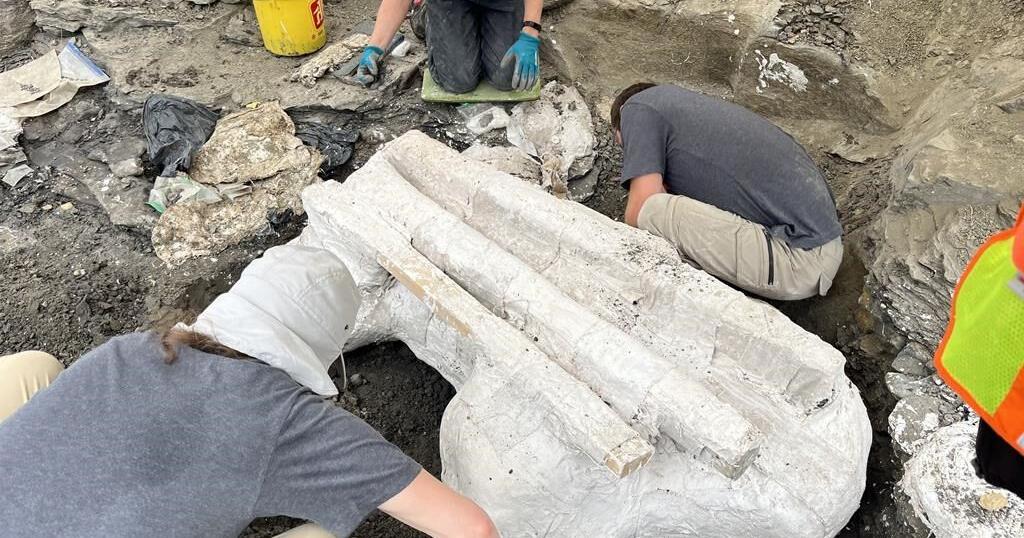

It’s a dinosaur that roamed Alberta’s badlands more than 70 million years ago, sporting a big, bumpy, bony head the size of a baby elephant.
On Wednesday, paleontologists near Grande Prairie pulled its 272-kilogram skull from the ground.
They call it “Big Sam.”
The adult Pachyrhinosaurus is the second plant-eating dinosaur to be unearthed from a dense bonebed belonging to a herd that died together on the edge of a valley that now sits 450 kilometres northwest of Edmonton.
It didn’t die alone.
“We have hundreds of juvenile bones in the bonebed, so we know that there are many babies and some adults among all of the big adults,” Emily Bamforth, a paleontologist with the nearby Philip J. Currie Dinosaur Museum, said in an interview on the way to the dig site.
She described the horned Pachyrhinosaurus as “the smaller, older cousin of the triceratops.”
“This species of dinosaur is endemic to the Grand Prairie area, so it’s found here and nowhere else in the world. They are … kind of about the size of an Indian elephant and a rhino,” she added.
The head alone, she said, is about the size of a baby elephant.
The discovery was a long time coming.
The bonebed was first discovered by a high school teacher out for a walk about 50 years ago. It took the teacher a decade to get anyone from southern Alberta to come to take a look.
“At the time, sort of in the ’70s and ’80s, paleontology in northern Alberta was virtually unknown,” said Bamforth.
When paleontogists eventually got to the site, Bamforth said, they learned “it’s actually one of the densest dinosaur bonebeds in North America.”
“It contains about 100 to 300 bones per square metre,” she said.
Paleontologists have been at the site sporadically ever since, combing through bones belonging to turtles, dinosaurs and lizards. Sixteen years ago, they discovered a large skull of an approximately 30-year-old Pachyrhinosaurus, which is now at the museum.
About a year ago, they found the second adult: Big Sam.
Bamforth said both dinosaurs are believed to have been the elders in the herd.
“Their distinguishing feature is that, instead of having a horn on their nose like a triceratops, they had this big, bony bump called a boss. And they have big, bony bumps over their eyes as well,” she said.
“It makes them look a little strange. It’s the one dinosaur that if you find it, it’s the only possible thing it can be.”
The genders of the two adults are unknown.
Bamforth said the extraction was difficult because Big Sam was intertwined in a cluster of about 300 other bones.
The skull was found upside down, “as if the animal was lying on its back,” but was well preserved, she said.
She said the excavation process involved putting plaster on the skull and wooden planks around if for stability. From there, it was lifted out — very carefully — with a crane, and was to be shipped on a trolley to the museum for study.
“I have extracted skulls in the past. This is probably the biggest one I’ve ever done though,” said Bamforth.
“It’s pretty exciting.”
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Sept. 25, 2024.
The Canadian Press. All rights reserved.
News
The ancient jar smashed by a 4-year-old is back on display at an Israeli museum after repair
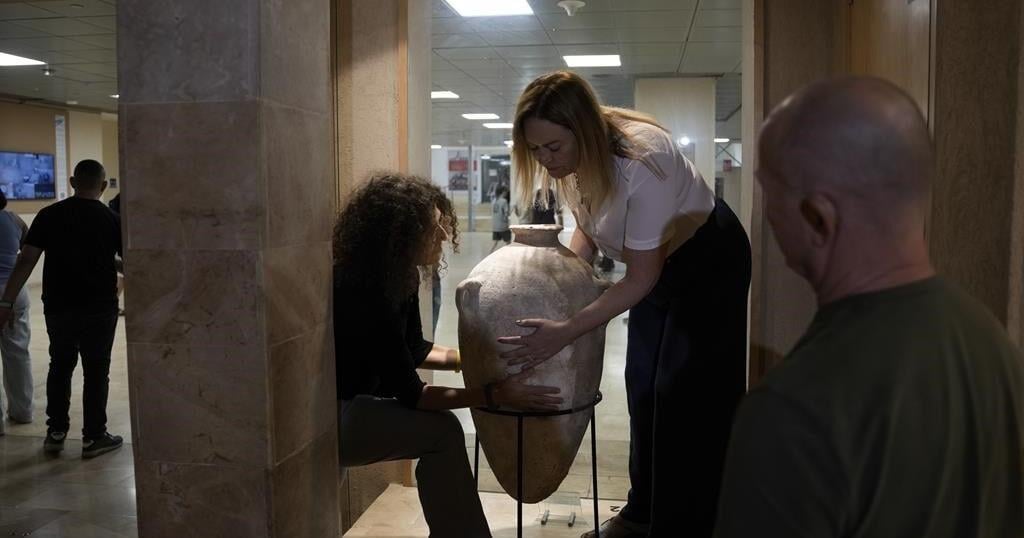

TEL AVIV, Israel (AP) — A rare Bronze-Era jar accidentally smashed by a 4-year-old visiting a museum was back on display Wednesday after restoration experts were able to carefully piece the artifact back together.
Last month, a family from northern Israel was visiting the museum when their youngest son tipped over the jar, which smashed into pieces.
Alex Geller, the boy’s father, said his son — the youngest of three — is exceptionally curious, and that the moment he heard the crash, “please let that not be my child” was the first thought that raced through his head.
The jar has been on display at the Hecht Museum in Haifa for 35 years. It was one of the only containers of its size and from that period still complete when it was discovered.
The Bronze Age jar is one of many artifacts exhibited out in the open, part of the Hecht Museum’s vision of letting visitors explore history without glass barriers, said Inbal Rivlin, the director of the museum, which is associated with Haifa University in northern Israel.
It was likely used to hold wine or oil, and dates back to between 2200 and 1500 B.C.
Rivlin and the museum decided to turn the moment, which captured international attention, into a teaching moment, inviting the Geller family back for a special visit and hands-on activity to illustrate the restoration process.
Rivlin added that the incident provided a welcome distraction from the ongoing war in Gaza. “Well, he’s just a kid. So I think that somehow it touches the heart of the people in Israel and around the world,“ said Rivlin.
Roee Shafir, a restoration expert at the museum, said the repairs would be fairly simple, as the pieces were from a single, complete jar. Archaeologists often face the more daunting task of sifting through piles of shards from multiple objects and trying to piece them together.
Experts used 3D technology, hi-resolution videos, and special glue to painstakingly reconstruct the large jar.
Less than two weeks after it broke, the jar went back on display at the museum. The gluing process left small hairline cracks, and a few pieces are missing, but the jar’s impressive size remains.
The only noticeable difference in the exhibit was a new sign reading “please don’t touch.”
The Canadian Press. All rights reserved.
-

 News20 hours ago
News20 hours agoA tiny grain of nuclear fuel is pulled from ruined Japanese nuclear plant, in a step toward cleanup
-

 News21 hours ago
News21 hours agoCanadanewsmedia news November 07, 2024: Canada’s health-care spending to reach $372 billion in 2024
-

 Sports20 hours ago
Sports20 hours agoDeMar DeRozan scores 27 points to lead the Kings past the Raptors 122-107
-

 Sports20 hours ago
Sports20 hours agoPWHL unveils game jerseys with new team names, logos
-

 News20 hours ago
News20 hours agoWho ruined Hobo Hot Springs? Ministry investigates as mystery roils Harrison, B.C.
-

 News14 hours ago
News14 hours agoAlberta forestry minister says wolverine, lynx trapping limits lifted to gather data
-

 News15 hours ago
News15 hours agoCourt order will compel release of records in Dye & Durham competition probe
-

 News20 hours ago
News20 hours agoHundreds will lose access to safe consumption when some Toronto sites close: study





















