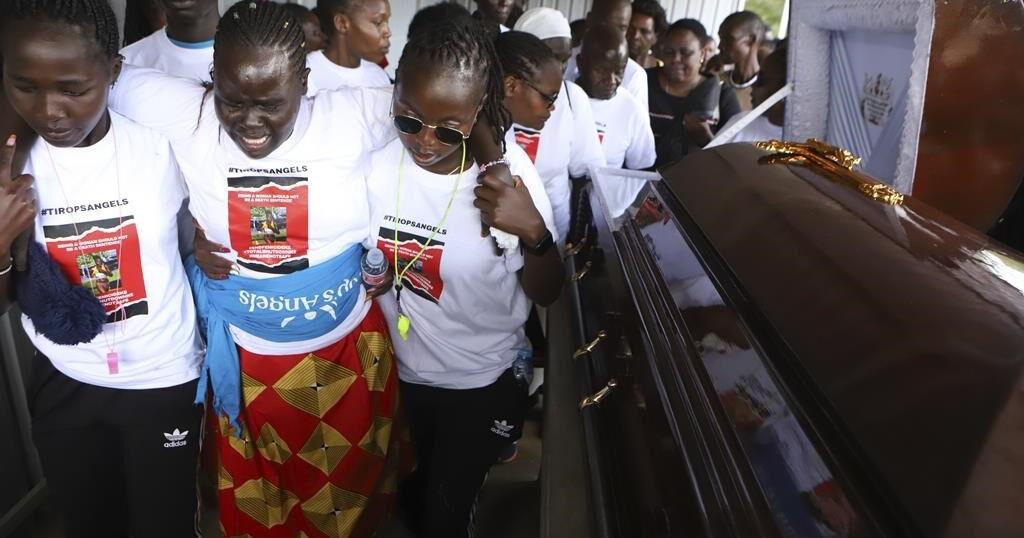
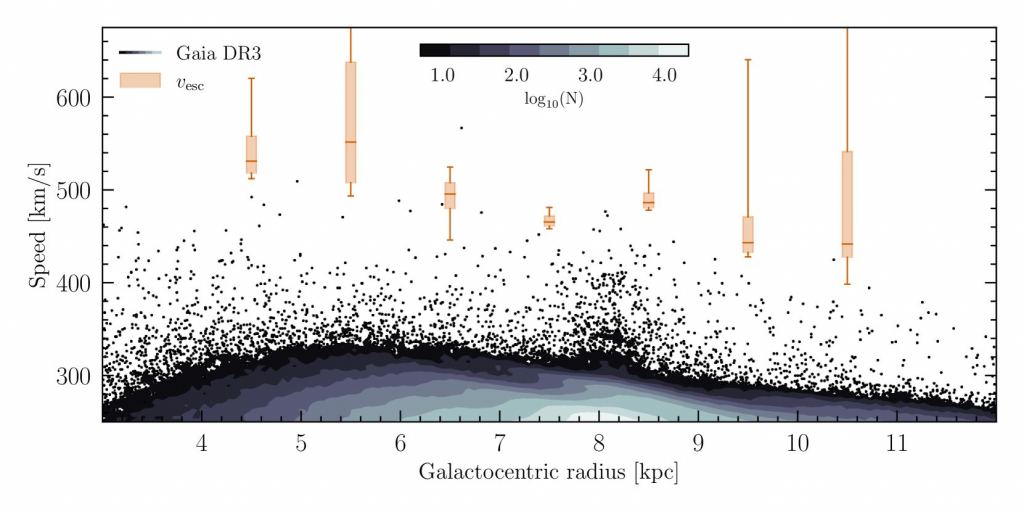
NAIROBI, Kenya (AP) — The body of Ugandan Olympic athlete Rebecca Cheptegei — who died after being set on fire by her partner in Kenya — was received Friday by family and anti-femicide crusaders, ahead of her burial a day later.
Cheptegei’s family met with dozens of activists Friday who had marched to the Moi Teaching and Referral Hospital’s morgue in the western city of Eldoret while chanting anti-femicide slogans.
She is the fourth female athlete to have been killed by her partner in Kenya in yet another case of gender-based violence in recent years.
Viola Cheptoo, the founder of Tirop Angels – an organization that was formed in honor of athlete Agnes Tirop, who was stabbed to death in 2021, said stakeholders need to ensure this is the last death of an athlete due to gender-based violence.
“We are here to say that enough is enough, we are tired of burying our sisters due to GBV,” she said.
It was a somber mood at the morgue as athletes and family members viewed Cheptegei’s body which sustained 80% of burns after she was doused with gasoline by her partner Dickson Ndiema. Ndiema sustained 30% burns on his body and later succumbed.
Ndiema and Cheptegei were said to have quarreled over a piece of land that the athlete bought in Kenya, according to a report filed by the local chief.
Cheptegei competed in the women’s marathon at the Paris Olympics less than a month before the attack. She finished in 44th place.
Cheptegei’s father, Joseph, said that the body will make a brief stop at their home in the Endebess area before proceeding to Bukwo in eastern Uganda for a night vigil and burial on Saturday.
“We are in the final part of giving my daughter the last respect,” a visibly distraught Joseph said.
He told reporters last week that Ndiema was stalking and threatening Cheptegei and the family had informed police.
Kenya’s high rates of violence against women have prompted marches by ordinary citizens in towns and cities this year.
Four in 10 women or an estimated 41% of dating or married Kenyan women have experienced physical or sexual violence perpetrated by their current or most recent partner, according to the Kenya Demographic and Health Survey 2022.